Dmitri Mendeleev is one of the pioneers of modern chemistry. Despite the fact that most Russians know Dmitri Mendeleev mainly for his work in alcohol testing and vodka production, he was a brilliant scientist who revolutionised our understanding of properties of atoms. He was never awarded the Nobel Prize; nevertheless he is considered one of the greatest chemists, also having element 101 named after him.
By year 1860 about 60 elements were known and more and more were being discovered. Many people started thinking about listing these elements according their properties. They discovered that some elements behave in a similar way, such as Li, Na, K, (alkali metals as we call them today) react vigorously with water. They called these groups of elements “triads”. It was also noticed that when elements are listed according to their atomic weight, similar properties recurred in intervals of eight. Some people tried to make a system based on these rules. There was even an attempt to align the elements according to their valency i.e. how many bonds they tend do form in a compound. However, these systems always had some flaw in them (mainly due to the fact that many elements were still to be discovered). And this is where Mendeleev got his chance for a breakthrough.
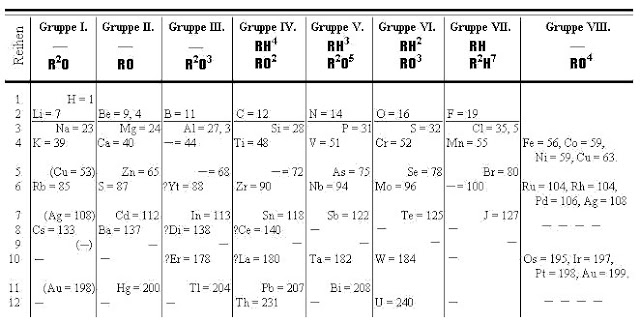
Mendeleev was not aware of any other work on periodic table that was going on during that time, but based his periodic table on several trends that were already discovered before. For example he arranged the elements according to their atomic mass and valency, and he also grouped elements with similar properties (such as halogens) together. However, the reason why his periodic table is so special is that he left out spaces for yet unknown elements that were discovered many years after he died. He also connected the position of an element in the periodic table with its properties and this way he actually correctly predicted behaviour of many unknown elements. At first, his work was not taken seriously, until the discovery of Gallium (Mendeleev called “eka-aluminium” meaning that it lies below aluminium in the periodic table). Mendeleev predicted its density, atomic radius and its chemical properties accurately.
Mendeleev’s periodic table of elements
Mendeleev was not always correct in his assumptions. For example he listed tellurium after iodine because tellurium has lower atomic mass. Nevertheless he managed to set up a functional system of elements that persisted in slightly changed form until today despite the fact that some fundamentals theories were invented after his death and this way he largely contributed to chemistry becoming a modern science.
http://www.chem.tamu.edu/class/majors/tutorialnotefiles/periodic.htm
No comments:
Post a Comment